Corrosion Behaviour
Author: Time:2023-05-17
Corrosion behaviour of heat exchangersThe corrosion resistance of aluminium heat exchangers depends on the (electro-) chemical interaction of the entire system, the micro-structure of the core material and environmental factors. The micro-structure, which is influenced by the chemical composition and the processing, has a significant impact on the mechanism of corrosion. The severe environmental conditions to which aluminium heat exchangers may be exposed have a considerable effect on lifetime. Both internal corrosion due to heat exchanging agents(e.g. Refrigerants and coolants) and external corrosion relating to the environment(e.g. Salt, water) can cause perforations and leaks.
Pitting corrosion
Heat exchangers often suffer from pitting corrosion, as in the presence of an electrolyte the surface brazing material is removed at localized points and this results in the development of cavities. The primary cause of pitting is a difference in the corrosion potential created by an inhomogeneity either in or on the material surface.
Waterside corrosion
Waterside corrosion on the inner side of a tube can be controlled sufficiently through the use of the proper cooling liquid with appropriate inhibitors. When applied to the core, waterside clad allys such as EN AW-1050 or EN AW-7072 can improve internal corrosion resistance.
Air side corrosion
All approaches aimed at enhancing the corrosion properties of aluminium brazing sheet materials are intended to mitigate the deleterious pitting mechanism into a less harmful corrosive attack. SIGNI rolling has developed special top-clad aluminum brazing sheet and coil, which incorporates special chemistries with tailored thermo-mechanical processing. This well designed combination between chemical composition and the production route considerably improves the corrosion resistance of these Long life alloys.

Galvanic Protection
The principle of galvanic protection is commonly applied with regard to the critical components of the heat exchanger. When in contact with an electrolyte, a less noble (anodic) alloy corrodes preferably in comparison with a noble(cathodic) alloy. Corrosion prevention requires careful selection of alloy combinations. Depending on the electro-chemical potentials of the post-brazed materials in use, the corrosion attack on the single components can be controlled.
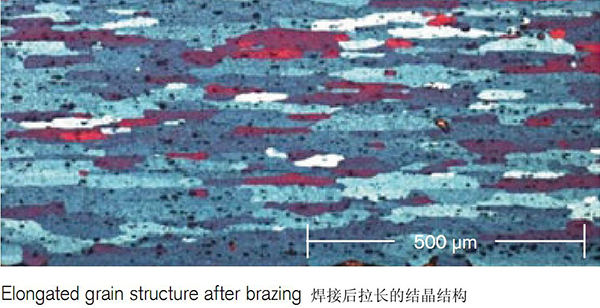
Modification of the Micro-structure
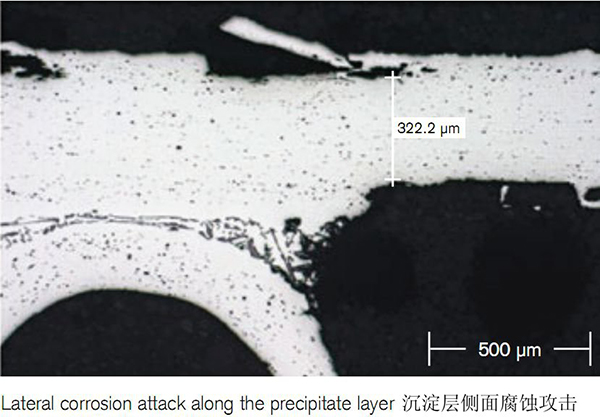
As grain boundaries represent the path along which corrosion proceeds, elongated grains enhance the long life performance of the material. The precipitation of Al-Mn-Si particles adjacent to the core/filler interface has a further positive impact on the corrosions resistance. This is because the precipitate layer has lower corrosion potential than the residual core and thus acts as a sacrificial layer.
Material Selection
The electro-chemical potentials of heat exchanger materials may indicate the corrosiveness but does not include the influence of the micro-structure on the corrosion.
Accelerated corrosion tests(SWAA-Test) allows SIGNI to predict the durability of heat exchangers.